What is Decision-Making in C#?
C# provides numerous declarations on decision making to help the C # Program flow under certain logical conditions. The following statements are included in the C # decision making.
Decision making structures will require the programmer to specify one or more program conditions for evaluation or testing, together with a statement or statements to be made if the requirement is determined to be true, and optionally, if the situation is determined to be incorrect, other statements will be performed.
- if statement
- if-else statement
- else if statement
This is followed by the typical structure of decision-making in most programming languages:
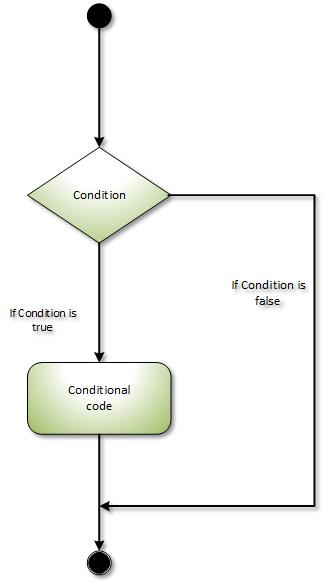
C# If Statement
The C# if statement checks the condition. If condition is true it is executed.
Syntax:
if(condition){
//code to be executed
}
Example:
using System;
public class IfExample
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int num = 20;
if (num % 2 == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("It is even number");
}
}
}
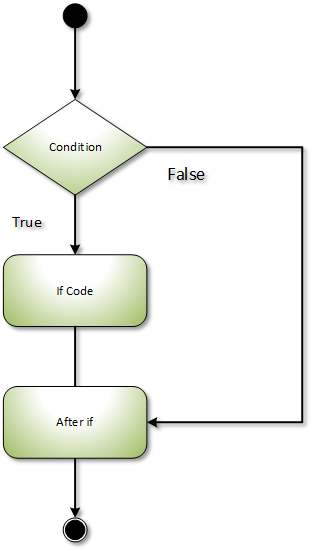
C# If-else Statement
The C# if-else statement also checks the condition. If the condition is true then, if statement execute otherwise (if condition is false), else block statement execute.
Syntax:
if(condition){
//code if condition is true
}else{
//code if condition is false
}
Example:
using System;
public class IfExample
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int num = 15;
if (num % 2 == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("It is even number");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("It is odd number");
}
}
}
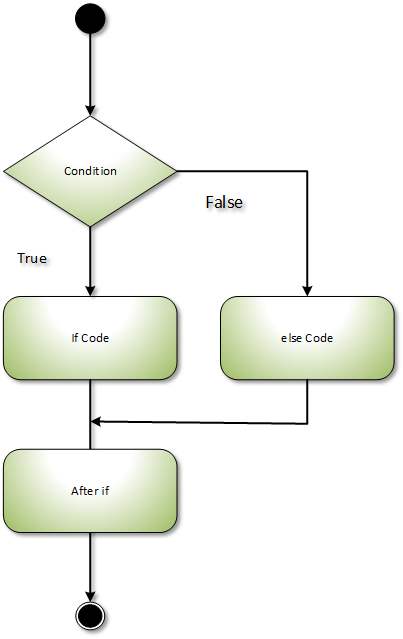
C# else-If statement
If we want to check another condition in the else part, the ' If ' statement can follow an ' else ' statement as well.
Syntax:
if(condition1){
//code to be executed if condition1 is true
}else if(condition2){
//code to be executed if condition2 is true
}
else if(condition3){
//code to be executed if condition3 is true
}
...
else{
//code to be executed if all the conditions are false
}
Example:
using System;
namespace DecisionMaking {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
//* local variable definition */
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
/* check the boolean condition */
if (a == 100) {
/* if condition is true then check the following */
if (b == 200) {
/* if condition is true then print the following */
Console.WriteLine("Value of a is 100 and b is 200");
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Exact value of a is : {0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("Exact value of b is : {0}", b);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
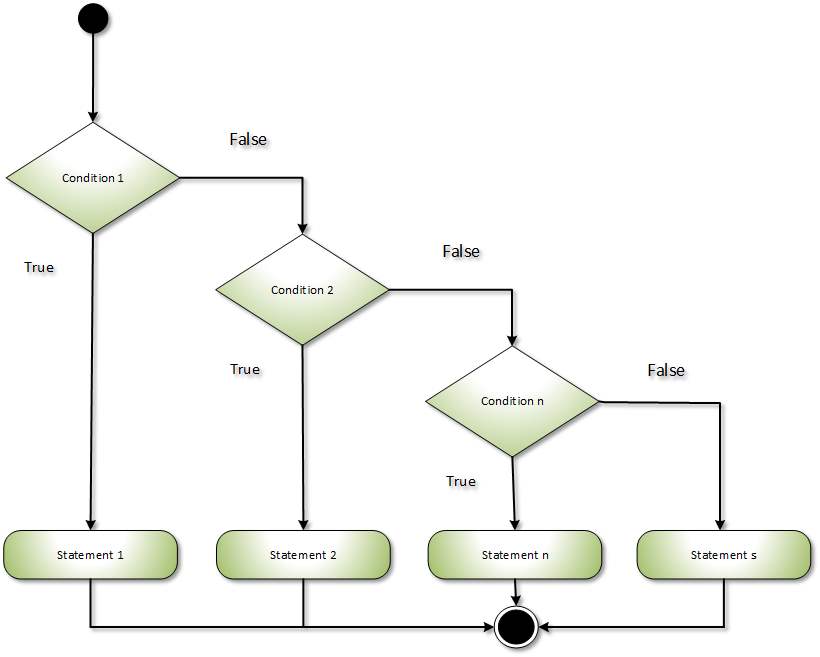
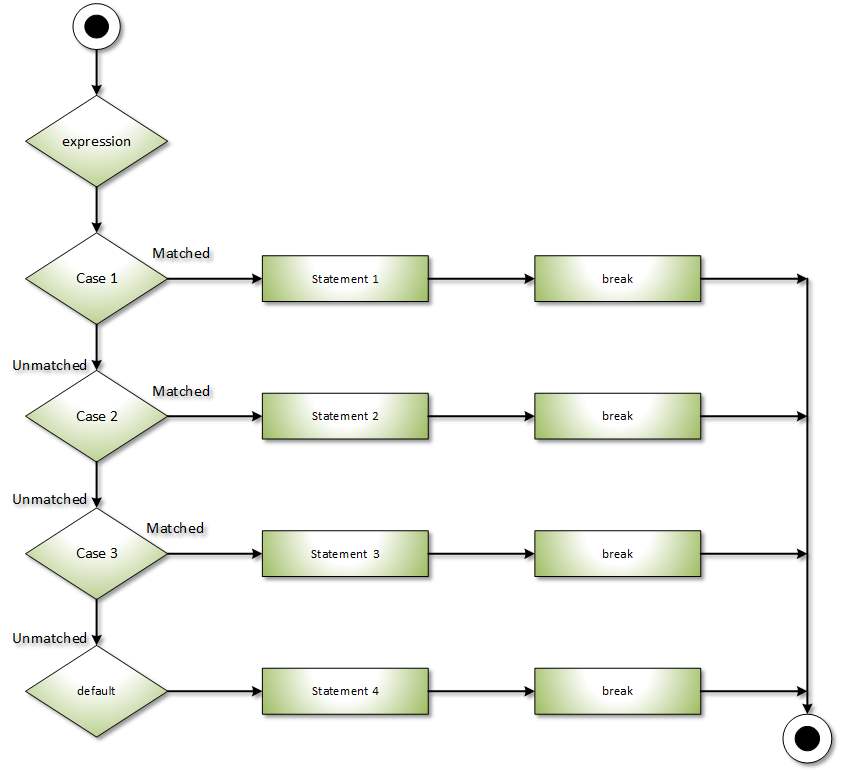
C# switch case
The switch case in C# execute one statement from several conditions. It is like a if-else-if command in C#.
Syntax:
switch(expression){
case value1:
//code to be executed;
break;
case value2:
//code to be executed;
break;
......
default:
//code to be executed if all cases are not matched;
break;
}
Example:
using System;
namespace SwitchCaseExample {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
/* local variable definition */
char grade = 'B';
switch (grade) {
case 'A':
Console.WriteLine("Excellent!");
break;
case 'B':
case 'C':
Console.WriteLine("Well Done");
break;
case 'D':
Console.WriteLine("You Passed");
break;
case 'F':
Console.WriteLine("Better Try Again");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Invalid Grade");
break;
}
Console.WriteLine("Your grade is {0}", grade);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
