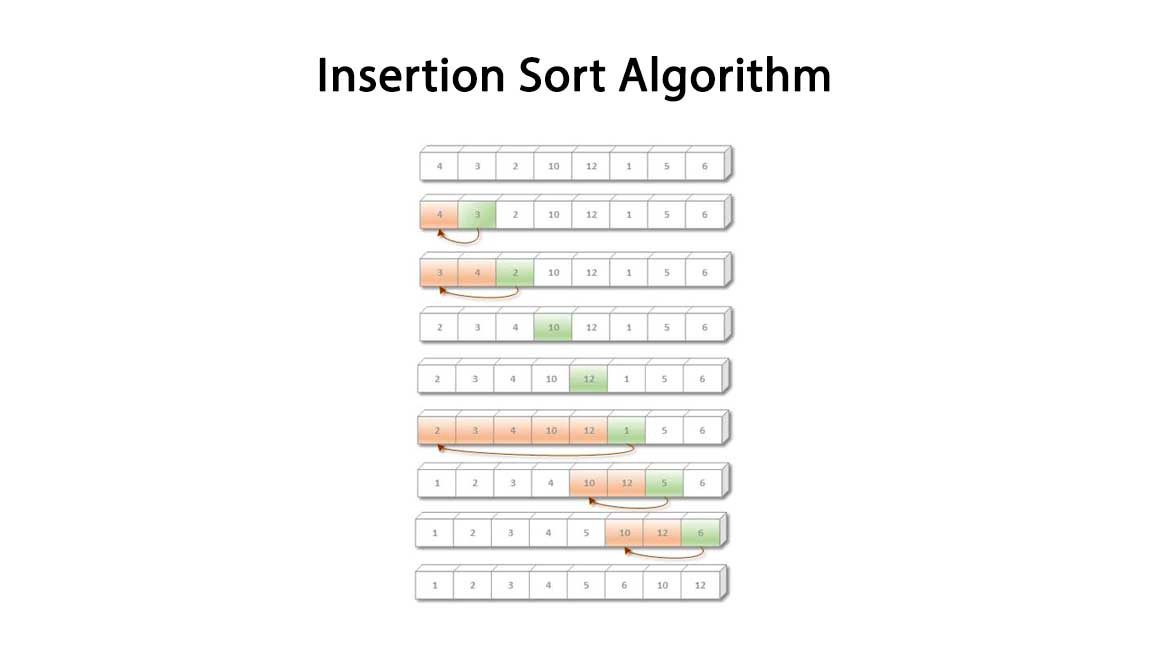
Question: What is string ? How can we declare & initialize the strings?
Answer: String is a collection of characters.
A string is a sequence of characters. Any sequence or set of characters defined within double quotation symbols
is a constant string. Strings are stored in memory as ASCII codes of characters that make up the string appended with ‘\0’ (null character). ‘\0 ’ is not same as ‘0’. ASCII value of null character (‘\0 ’) is zero & value of ‘0’ is 35.
A string variable is always declared as an array. The variable is any valid C variable name the syntax for declaring a string variable is given below :
Char string-variable[size];
Where the size is the number of characters in the string-variables.
For example , consider the declaration of string variables given below:
char name[25];
char result[15];
The compiler provides a null character (‘\0’) at the end of the string while assigning a character string
to a character array.
It is possible to initialize the string variables while declaring.
For example, consider the initialization of string variable at the time of declaration as given below:
char name[6] = "School";
The variable name is a character array of 6 elements of storage. Therefore, the above initialization statement can be rewritten as follows:
char name[6] = {'S','c','h','o','o','l','\0'};
Below is the memory representation of a string "School".
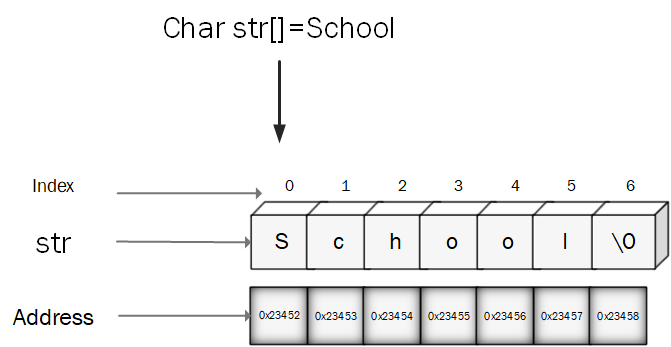
While initializing a character array, by listing its elements as above, the null terminator ('\0') should be supplied explicitly.